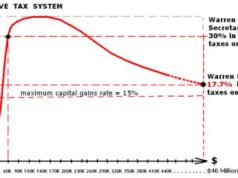
Introduction
Tax brackets are used to determine the amount of tax an individual owes based on their income. Knowing your tax bracket can help you plan for taxes and make decisions regarding your finances. However, determining which tax bracket you fall in can be overwhelming. Here’s a guide to help you figure it out.
What are Tax Brackets?
A tax bracket is a range of income levels that determine how much tax an individual owes. Each bracket has a different tax rate, and as your income increases, the percentage paid in taxes may increase as well.
How to Determine Your Tax Bracket
To determine your tax bracket, you will need to know your taxable income, which is defined as your total income minus deductions. Once you have your taxable income, you can refer to the tax bracket chart for your filing status to determine in which bracket you fall.
Tax Bracket Chart
The following is a tax bracket chart for the 2021 tax year:
Single taxpayers:
– 10% tax bracket: $0 to $9,950
– 12% tax bracket: $9,951 to $40,525
– 22% tax bracket: $40,526 to $86,375
– 24% tax bracket: $86,376 to $164,925
– 32% tax bracket: $164,926 to $209,425
– 35% tax bracket: $209,426 to $523,600
– 37% tax bracket: $523,601 or more
Married taxpayers filing jointly:
– 10% tax bracket: $0 to $19,900
– 12% tax bracket: $19,901 to $81,050
– 22% tax bracket: $81,051 to $172,750
– 24% tax bracket: $172,751 to $329,850
– 32% tax bracket: $329,851 to $418,850
– 35% tax bracket: $418,851 to $628,300
– 37% tax bracket: $628,301 or more
Married taxpayers filing separately:
– 10% tax bracket: $0 to $9,950
– 12% tax bracket: $9,951 to $40,525
– 22% tax bracket: $40,526 to $86,375
– 24% tax bracket: $86,376 to $164,925
– 32% tax bracket: $164,926 to $209,425
– 35% tax bracket: $209,426 to $314,150
– 37% tax bracket: $314,151 or more
Conclusion
Determining which tax bracket you fall in is an essential step in understanding your tax liability. Knowing your tax bracket can help you take control of your finances better. Be sure to stay updated on tax laws and any changes to the tax bracket chart, so you can adjust your finances accordingly. Consult a tax professional to help you manage your taxes.
What is Income Tax?
Income Tax is a variety of tax that levies the fulfillment of required taxation in correlation with an individual’s earned income from labor. Income tax is classified as a ‘progressive’ tax due to the fact that the required income tax payments are contingent upon the gross amount of income earned by that individual. Within a tax-based society, Taxes may be incurred for a variety of reasons and through a variety of means; taxes can range in their collection process, procedure of payment, and respective rates.
What is a Tax Bracket?
While certain taxes may be required by the entire populace, other taxes may be required by a finite group of individuals. Within the United States of America, a system of classification has been instated that allows for the individual categorization – through collective analysis – of Individual tax payers; this classification places individual tax payers into a corresponding tax bracket.
How is a Tax Bracket Classified?
A progressive tax is a type of tax that is considered to fluctuate in accordance with any or all financial increases both in earnings and values; a tax that is progressive in nature illustrate a larger tax withholding to exist in tandem with larger earnings – in the United States, income tax laws operate as a progressive taxation system. Subsequent the establishment of a tax bracket system, individuals will be categorized in accordance to their respective, individual wage earnings.
How Many Tax Brackets Exist?
Currently, 6 Tax brackets exist within the taxation system employed by the United States of America; the range of tax brackets includes individuals earning no money to those earning the largest amount(s) of wages:
Bracket 1
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $0 – $8,025
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %10
Bracket 2
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $8,025 – $32,550
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %15
Bracket 3
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $32,550 – $78,850
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %25
Bracket 4
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $78,850 – $164,550
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %28
Bracket 5
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $164,550 – $357,700
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %33
Bracket 6
Applied Parameter of the Accumulated Annual Wage Earnings: Between $357,700 & over
Implicit Tax Rate Percentage: %35
Which Tax Forms Affect my Tax Bracket?
Rate-based Taxes are incurred in accordance with the amount of respective income earned by individual taxpayers. The following forms are tax forms that convey information that may affect current standing – and subsequent alteration – of tax classification through a tax bracket:
Form-1040: This form is considered to be the general income tax form within the United States, which is facilitated in order to convey the amount of personal earnings and income
Dependency Forms: A dependent is mentioned within income tax forms as a means to calculate the amount of earned income that may be potentially exhausted on individuals for whom the taxpayer claims responsibility
W-2 Form: This form substantiates the amount of taxes withheld as a result of respective labor, occupation, or profession